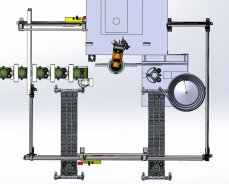
The Challenge
A three-shift operation. Repetitive loading of belt tensioners – a critical component of combustion engines – into a testing and finalization device. A confined working area of just 2 square meters. Inefficient use of operator time, with workers simply waiting for test sequences to finish, unable to contribute elsewhere in the meantime. All of these factors made this workstation the ideal candidate for automation.
Client Requirement
An automotive client approached us with the goal of automating the operation of a test line for belt tensioners, which had until then been running in uninterrupted three-shift mode. The manual operation led to significant productivity losses, as the worker had to wait idly for the testing cycle to finish. Meanwhile, belt tensioners are a critical safety component in engine design. The production line output components are used in final assembly Audi and Volkswagen cars.
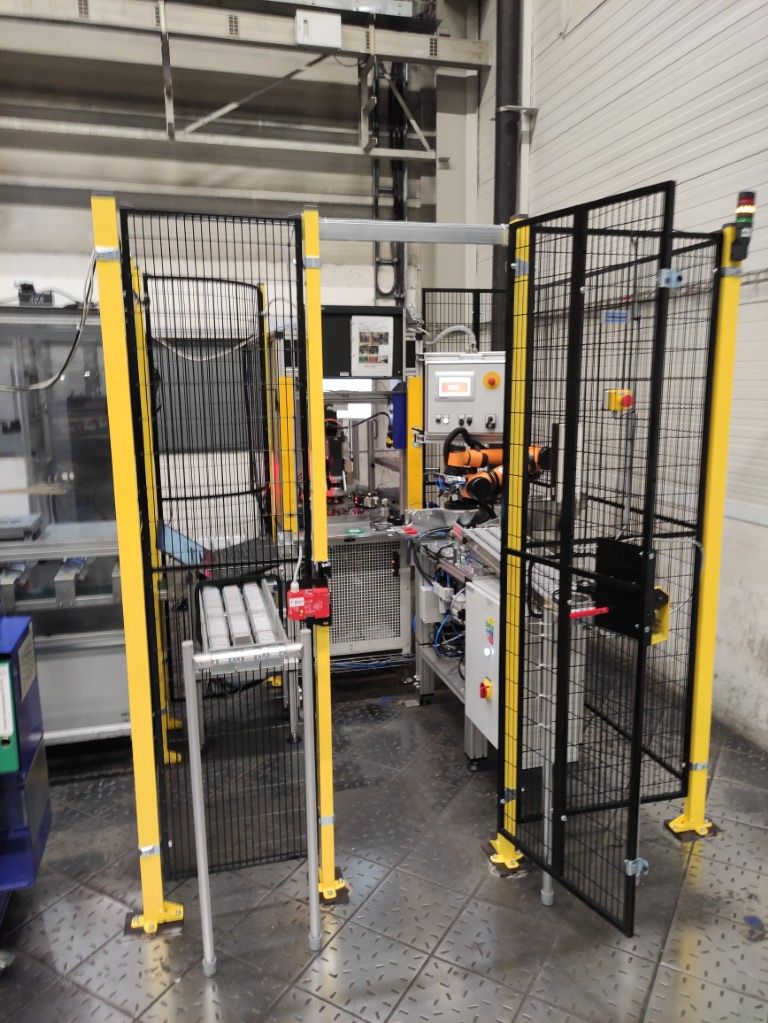
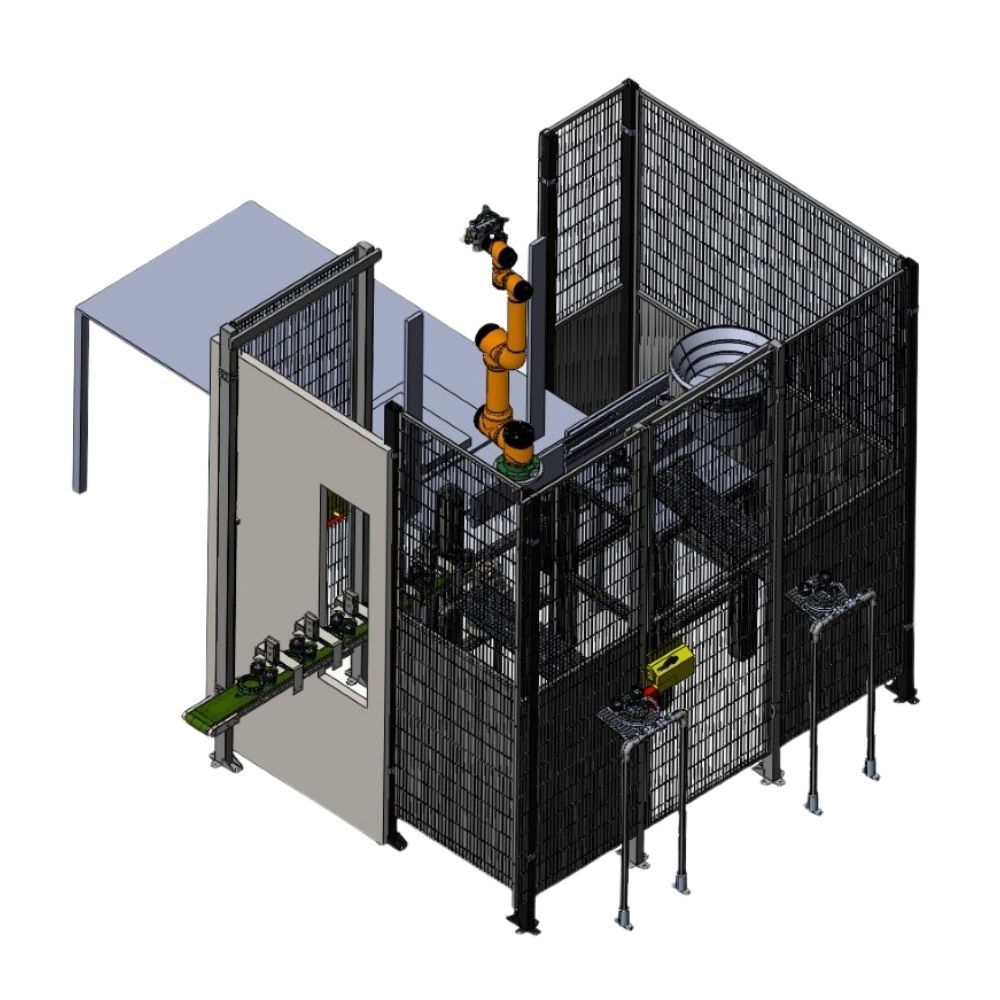

KINALI’s Solution
We designed and delivered a robotic workstation to automate the test device operation. The input to the station consists of belt tensioners and safety pins. While the pins are manually loaded into a vibratory feeder, the rest of the process – including pin insertion – is handled automatically. Tensioners are delivered fully automatically from the upstream assembly process.
The system accumulates incoming tensioners on an infeed conveyor with a buffer, which compensates for the difference in processing speeds between the assembly and testing stages. As testing is faster than assembly, this ensures a steady supply of parts without delays, even in case of interruptions in the assembly.
A collaborative AUBO i5 robot (payload 5 kg, reach 886 mm), equipped with a dual pneumatic Schunk JGZ 50 gripper, handles all part manipulation efficiently, helping increase overall throughput.
After a successful test, the robot places the tensioner into a pulley extension mechanism, where it is locked into position using an automated pin insertion system. Finished products are transferred to a gravity-driven OK conveyor and collected by an operator. Defective components are sent to a separate NOK conveyor.
Although collaborative robots typically do not require additional guarding, we chose to integrate safety fencing and covers in this case due to the high part weight, sharp edges, and use of a powerful pneumatic spreader, which posed potential injury risks in the event of contact.
Do you face a similar challenge in your production?
Get in touch with us. We will gladly help you design a custom automation solution that fits your needs.
Key Technical Components
| Robot | Collaborative robot AUBO i5 |
| Belt conveyor |
Part of the workstation infeed section
|
| Robot mounting station |
Mount with adjustable positioning
|
| Pin insertion system |
Automated placement after successful test
|
| Gravity conveyors |
Used for output part handling
|
| Safety features |
Integrated into the machine structure
|
Implementation Highlights
Seamless integration into existing infrastructure
The client required full compatibility with their current production line. Thanks to a modular approach, we were able to extend the system without building a new machine, saving both time and investment.
Manual fallback option
To ensure uninterrupted production, the system was designed to allow the robot to be quickly moved aside so that an operator can take over manual operation without interrupting the workflow.
Outcome
With the deployment of our robotic solution, the client eliminated downtime, increased process stability, and reduced operating costs. The project demonstrated that automation can be flexible and seamlessly integrated into existing workflows while maintaining manual operation as a backup option. The result is a robust, reliable, and efficient solution tailored for modern automotive manufacturing environments.




 MENU
MENU